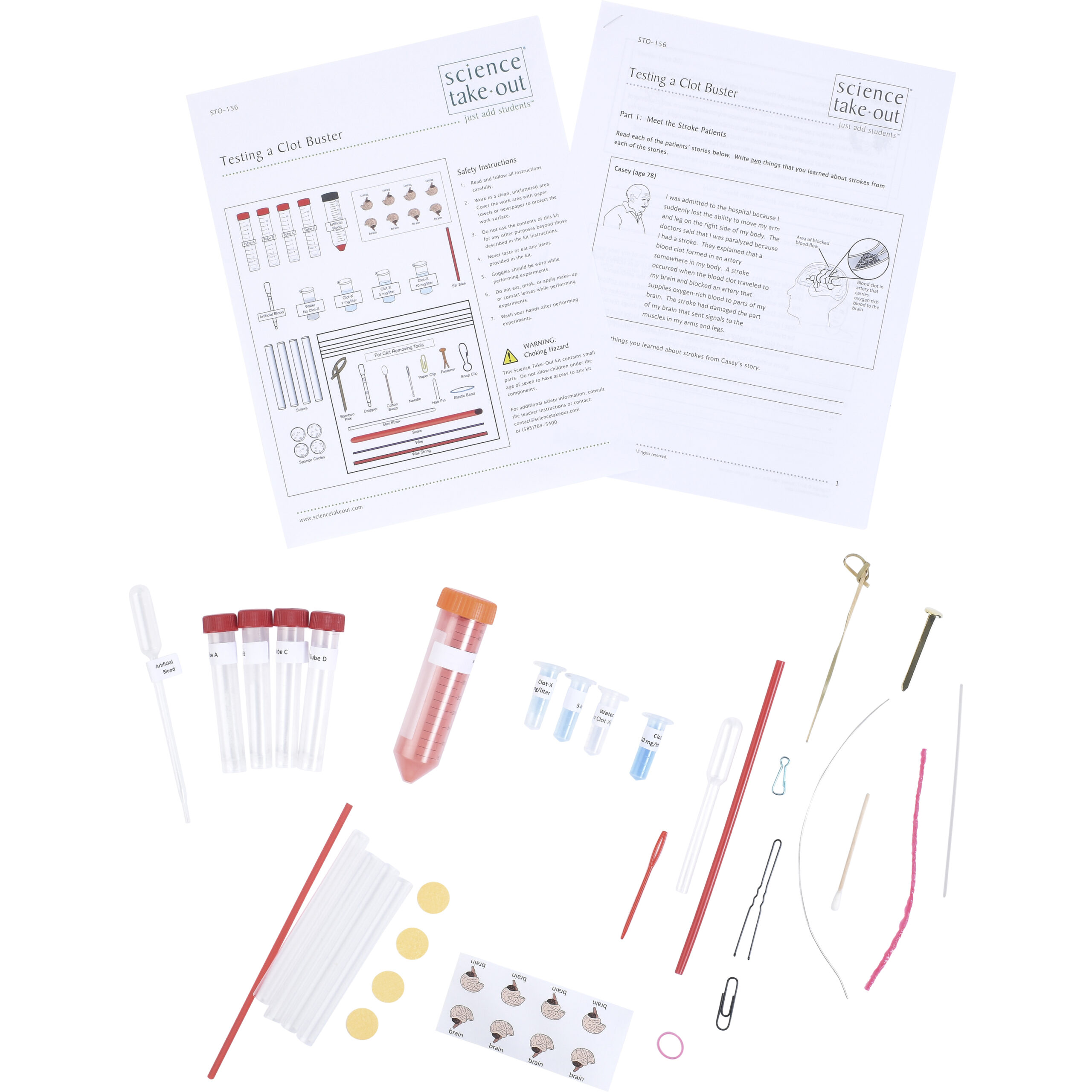
Testing a Clot Buster
$19.95 – $147.95
Test a new clot busting drug and engineer a clot removing tool.
Blood clots that block blood vessels to parts of the brain may cause serious brain damage. Clot-X is a simulated clot busting drug that dissolves blood clots.
- Analyze patients’ stories to learn about strokes and the use of “clot buster” drugs.
- Conduct simulated laboratory experiments to determine the concentration of Clot-X that is effective for treating strokes.
- Analyze data from research on the safety and effectiveness of Clot-X by creating a data table and a bar graph.
- Use models to engineer (design and evaluate) mechanical tools for restoring blood flow to blood vessels blocked by clots.
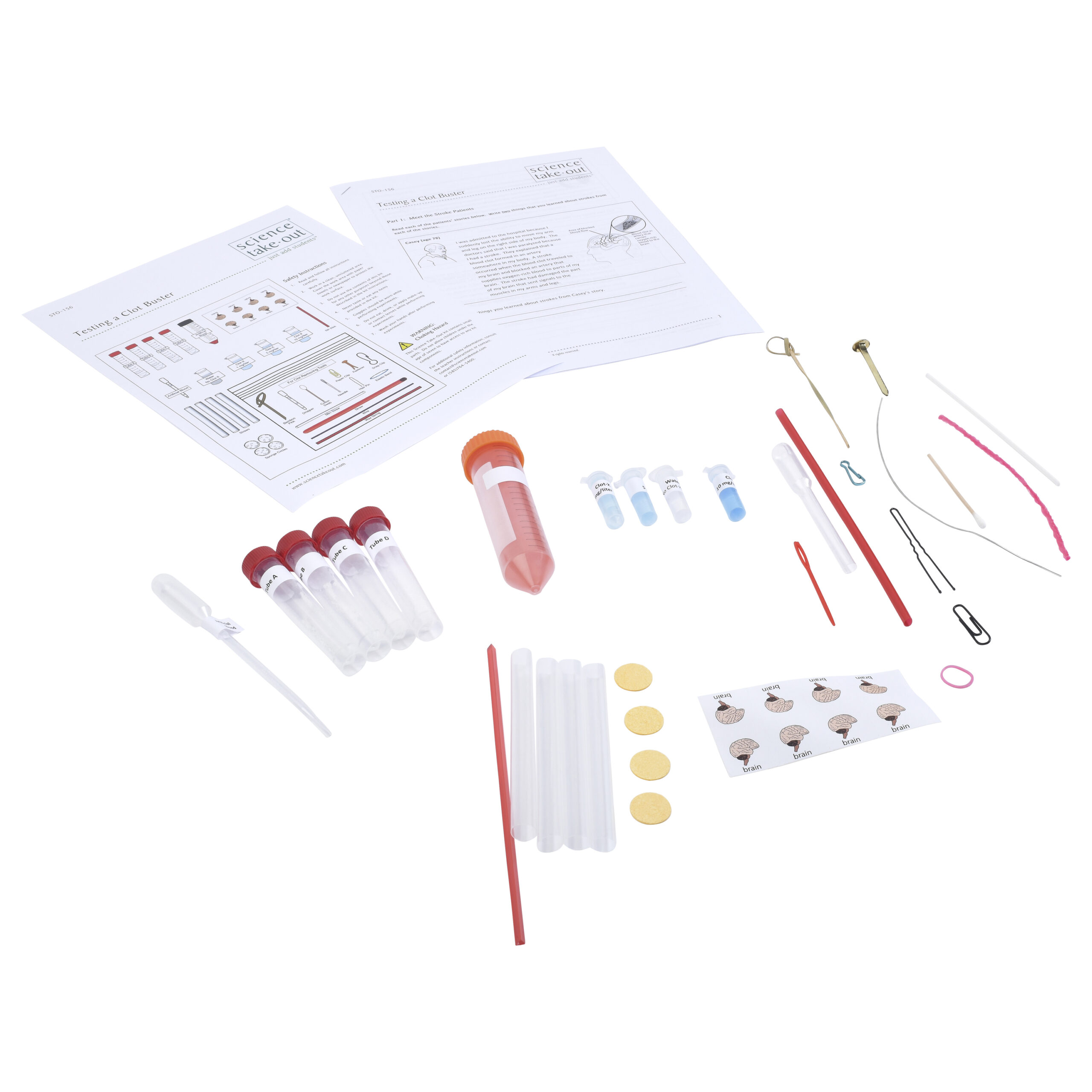
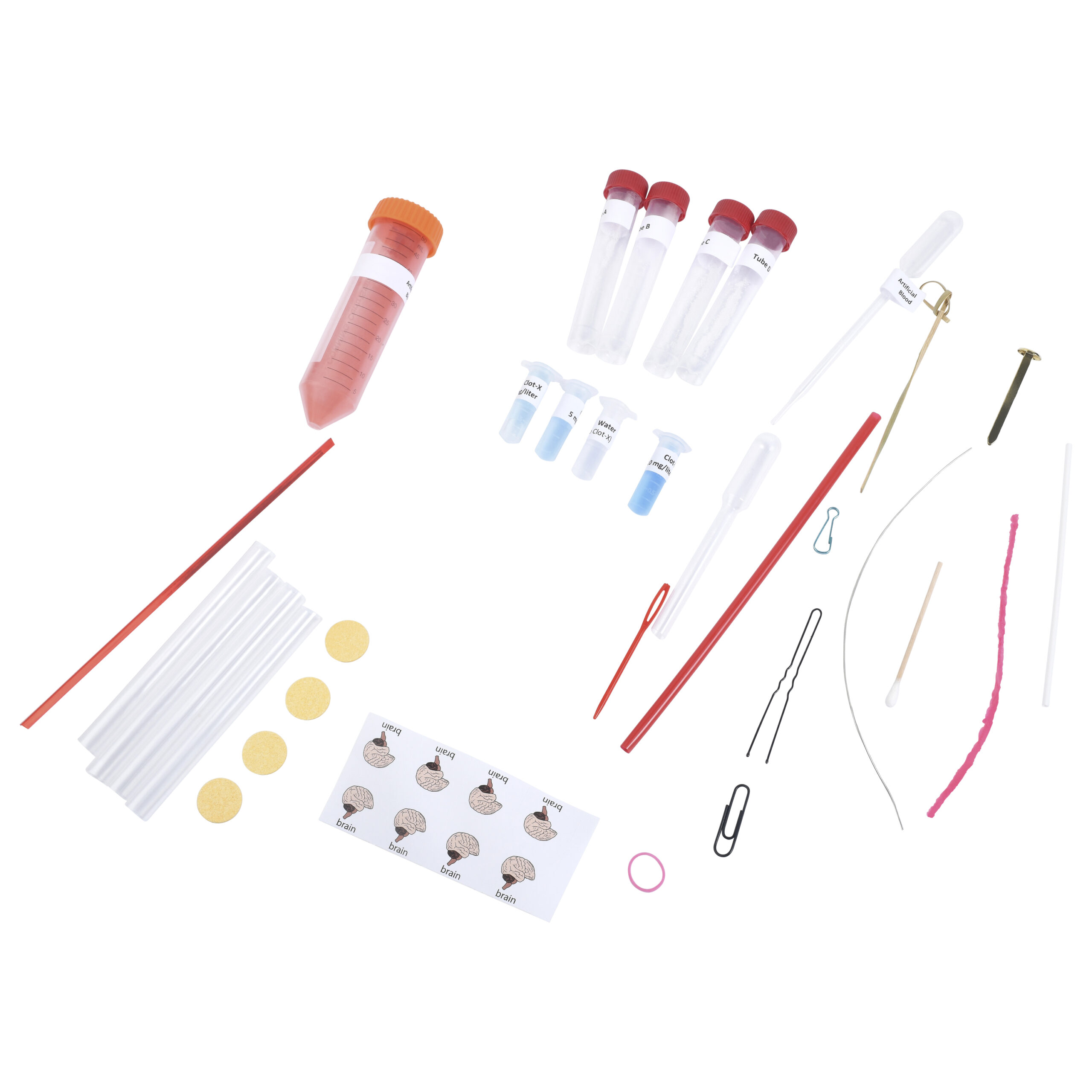
Kit Includes
- 4 tubes of “clotting protein”
- Graduated dropper
- Tube of “Artificial Blood”
- 1 microtube of water
- 3 microtubes of “Clot-X” (1, 5, and 10 mg/liter)
- 1 stir stick
- 4 straws
- 4 compressed sponges
- 4 brain labels
- materials for engineering clot removing tools
Also Required
- Calculator
- Transparent tape or masking tape
- Safety goggles
- Tap water
- Paper towels for clean-up
Quantity Discounts
Kits:
- 1 – 9 kits: $19.95 each
- 10 – 24 kits: $18.95 each
- 25+ kits: $17.96 each
Unassembled:
- 1 – 9 packs: $147.95 each
- 10+ packs: $140.55 each
Refills:
- 1 – 9 packs: $51.95 each
- 10+ packs: $49.35 each
Correlation to Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Shop by NGSS »
Performance Expectations:
MS-ETS1-3. Analyze data from tests to determine similarities and differences among several design solutions to identify the best characteristics of each that can be combined into a new solution to better meet the criteria for success.
Science & Engineering Practices
Analyzing and Interpreting Data - Analyze and interpret data to determine similarities and differences in findings.
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ETS1.B: Developing Possible Solutions - There are systematic processes for evaluating solutions with respect to how well they meet the criteria and constraints of a problem.
- Sometimes parts of different solutions can be combined to create a solution that is better than any of its predecessors.
ETS1.C: Optimizing the Design Solution - Although one design may not perform the best across all tests, identifying the characteristics of the design that performed the best in each test can provide useful information for the redesign process—that is, some of those characteristics may be incorporated into the new design.
Crosscutting Concepts
N/A