Can Insects Save the Planet?
$13.95 – $103.95
Follow the story of two college roommates as they explore possible protein sources in their diets.
- Evaluate different types of food protein sources and learn why protein sources are not all equal in value.
- Learn why a lack of essential amino acids can lead to malnutrition.
- Create and use models to simulate how proteins are processed in the body.
- Explore why crickets may be a valuable protein source for human health and for the health of the environment.
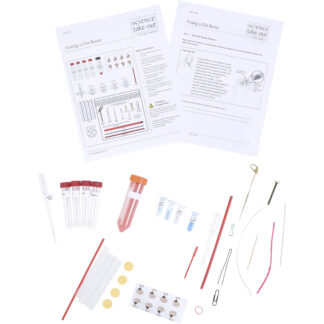
Kit Includes
- CHiPS Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) sheet
- Nutrition Facts Labels
- Protein Source Model Guide
- Bean Protein Processing Model sheet
- Cricket Protein Processing Model sheet
- Why CHiPs? sheet
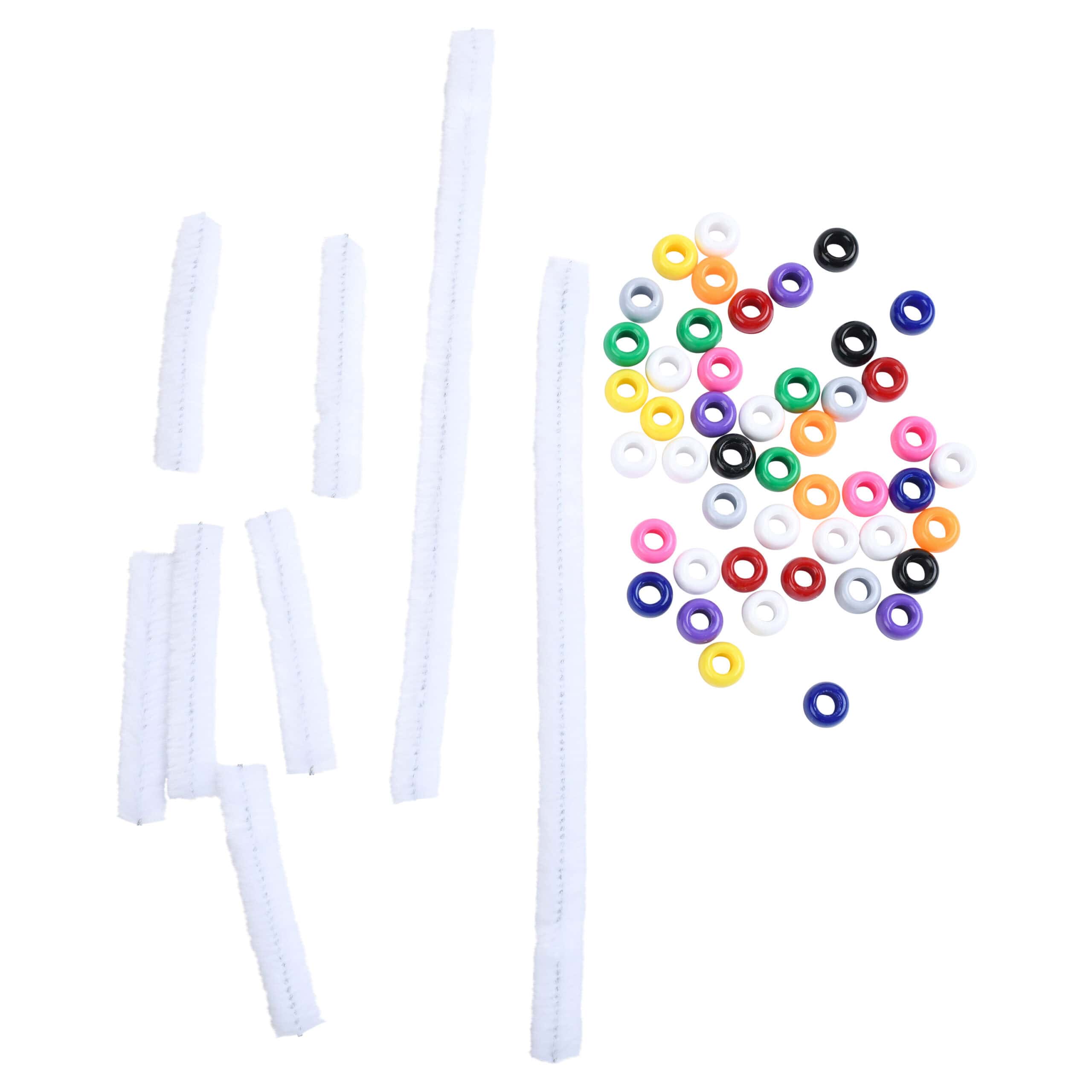
- Colored beads
- 2 long chenille stem pieces
- 6 short chenille stem pieces
Also Required
- Access to internet (optional)
Quantity Discounts
Kits:
- 1 – 9 kits: $13.95 each
- 10 – 24 kits: $13.25 each
- 25+ kits: $12.56 each
Unassembled:
- 1 – 9 packs: $103.95 each
- 10+ packs: $98.75 each
Correlation to Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Shop by NGSS »
Performance Expectations:
MS-LS1-7. Develop a model to describe how food is rearranged through chemical reactions forming new molecules that support growth and/or release energy as this matter moves through an organism.
MS-LS2-1. Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for the effects of resource availability on organisms and populations of organisms in an ecosystem.
Science & Engineering Practices
Developing and Using Models - Develop a model to describe unobservable mechanisms.
Analyzing and Interpreting Data - Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for a phenomenon.
Disciplinary Core Ideas
LS1.C: Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms
Within individual organisms, food moves through a series of chemical reactions in which it is broken down and rearranged to form new molecules, to support growth, or to release energy.
LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems
- Organisms, and populations of organisms, are dependent on their environmental interactions both with other living things and with nonliving factors.
- In any ecosystem, organisms and populations with similar requirements for food, water, oxygen, or other resources may compete with each other for limited resources, access to which consequently constrains their growth and reproduction.
- Growth of organisms and population increases are limited by access to resources.
PS3.D: Energy in Chemical Processes and Everyday Life
Cellular respiration in plants and animals involve chemical reactions with oxygen that release stored energy. In these processes, complex molecules containing carbon react with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and other materials.
Crosscutting Concepts
Energy and Matter - Matter is conserved because atoms are conserved in physical and chemical processes.
Cause and Effect - Cause and effect relationships may be used to predict phenomena in natural or designed systems.